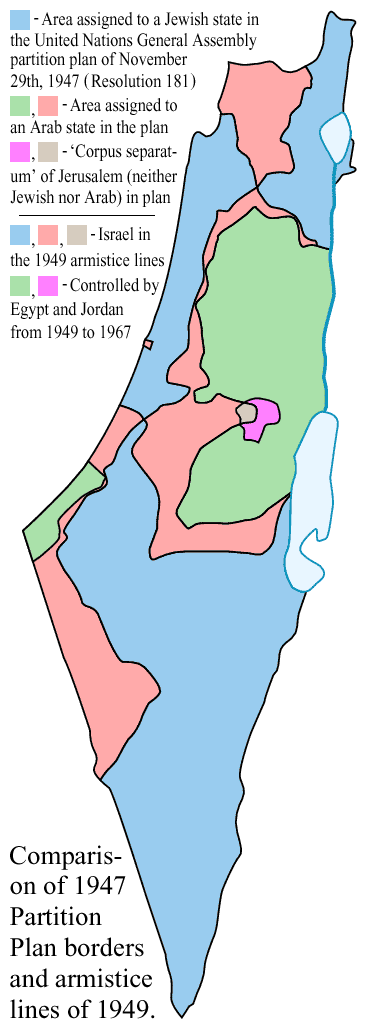
Cease-fire line vs. permanent border
The areas under Israeli control, as set by the agreements, encompassed about 78% of mandatory Palestine as it stood after the independence of Transjordan (now Jordan) in 1946. From the early 1920s to 1946, the British mandate of Palestine had also encompassed Transjordan, ruled under different arrangements from the area west of the Jordan river. Israel inside the armistice lines composed about 18% of this larger area including Transjordan. The areas of Palestine not occupied by Israel (the Gaza Strip and West Bank) were occupied by Egypt and Jordan respectively until 1967. See the related articles Occupation of the Gaza Strip by Egypt and Occupation of the West Bank and East Jerusalem by Jordan.
The armistice agreements were intended to serve only as interim agreements until replaced by permanent peace treaties. However, no peace treaties were actually signed until decades later. The armistice agreements, except for the one with Lebanon, were clear (at Arab insistence) that they were not creating permanent or de jure borders. The Egyptian-Israeli agreement stated "The Armistice Demarcation Line is not to be construed in any sense as a political or territorial boundary, and is delineated without prejudice to rights, claims and positions of either Party to the Armistice as regards ultimate settlement of the Palestine question."
The Jordanian-Israeli agreement stated: "... no provision of this Agreement shall in any way prejudice the rights, claims, and positions of either Party hereto in the peaceful settlement of the Palestine questions, the provisions of this Agreement being dictated exclusively by military considerations" (Art. II.2), "The Armistice Demarcation Lines defined in articles V and VI of this Agreement are agreed upon by the Parties without prejudice to future territorial settlements or boundary lines or to claims of either Party relating thereto." (Art. VI.9)